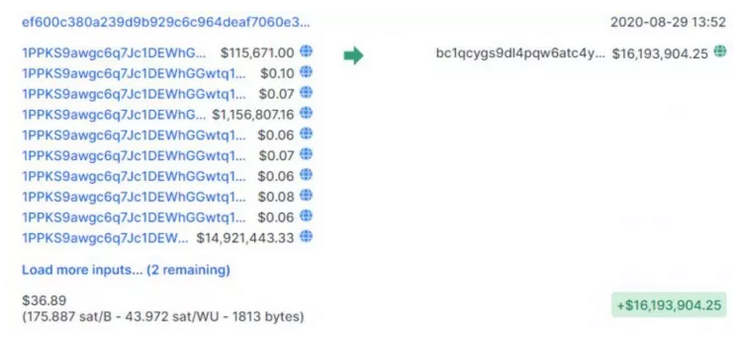
An Electrum user has reported the loss of 1,400 BTC worth $16 million to hacker after downloading an old version of the popular software wallet that is running on malicious servers.
The alleged hacker behind the huge theft initiated the transaction on 29th August 2020, paying $36.89 as transaction fees.
Details of the transaction can be found below as spotted by blockchain.com:
According to the CEO of Binance, Changpeng Zhao, popularly known as CZ, the exchange has already blacklisted the Bitcoin address.
CZ Binance tweeted, “Not your code, not your funds. Beware of this Electrrum official update. This guy lost 1400 BTC, and plenty of others lost funds too. We blacklisted the addresses involved, but…”
https://twitter.com/cz_binance/status/1300061833299070976
Hackers Have Long Taken Over Electrum Servers
The activity of hackers that are taking advantage of the vulnerability of the popular software wallet, Electrum, made headlines in 2019. Back then attackers released tons of botnets to target the wallet’s network.
It got to a point that the bad actors took over the majority of all the network’s nodes, which led to users receiving fake error messages prompting them to download malware-infected wallet software in the disguise of a security update.
According to Malwarebytes Labs, the hackers successfully stole seed data and upload it to a remote server:
“In addition to the theft of wallet data, any balance present in the wallet is sent to one of several pre-programmed public addresses under control of the attackers. The destination address chosen is dependent on the address format utilized by the infected users’ Electrum wallet.”
Upgrading the Electrum Software to Newest Version Is Essential
At that time, Thomas Voegtlin, the developer of Electrum, stressed the importance of upgrading the software wallet to the newest version, as all the versions older than 3.3.4 became vulnerable to phishing attacks.
“Electrum wallet users need to update the software to the latest version (3.3.4) from the official repository and be particularly careful with update or other warning messages that could be disguised phishing attempts.”
Join us on Twitter
Join us on Telegram
Join us on Facebook